An update on innovation strategy
Another conference on innovation landed last month in Barcelona: the European Networking Group with its Techscout 2014: Strategic Venturing and Innovation Excellence. Open Innovation directors from large corporates as Nestle, Unilever, General Mills, Shell and DSM shared their experience. The central question was: are we entering innovation maturity?
Behind this question the call: is it time to change our innovation strategy to cope with the disruptive changes? Innovation is a highly popularized word. Everyone is freely using and mentioning it. One should watch out for all those design thinking, brainstorming and ideation bubbles that try to capture this space. They are part of the process, an essential tool, just as necessary as the capacity to be creative, but most brainstorm and ideation results will be pivoted along the way to strengthen the more potential and strategic ones. An important success ingredient lies in tweaking what is not working correctly.
“ In a world of temporary advantage, stopping things – exiting declining advantages – is every bit as critical as starting things” – Rita Gunther McGrath
In the end, innovation is about creating new value as part of heading forward: concurring the future. The process after the ideation is where the challenge for innovation comes in through validation, prototyping and business model development- without it implementation and, hence, new added value will not be created.
Change as a Necessity
The future is all about transformation. It is being pushed by various megatrends and grand challenges, like urbanization, climate change, silver economy (ageing population) and connectivity. By emerging technology trends as featured by the WEF , where the end of screens is announced, since we are heading towards augmented environments or in lists of IEEE looking at the dominant technologies in 2022. It is being shaped by the actions and interactions of all players in an ecosystem, which leads to shifts and transitions. The world is becoming more and more smart, populated with a growing group of digital natives.
Nestle speaker Valerio Nannini referred to it as a VUCA world; Volatile, Uncertain, Complex and Ambiguous. The world is in constantly changing, disrupting  models cross industry boundaries. Causal relationships might be unclear, resulting in ´fighting´ against the “unknown unknowns”. There are ever more interconnected parts and variables, leading to higher degrees of complexity. Although a lot of data and knowledge is available, the megatrends create unexpected, unstable and most of all unknown situation, making predictions hard and leaving us with assumptions. Your position within the VUCA world depends on how much you know about the situation and how well you can predict the results of your actions. This explains the flourishing of predictive analytics to try to get a grasp. Next to that, we are in the era of beyond products: service, business model, digital and experience are dominating the business landscape. All this leads to an end for the old, established strategy paradigm.
models cross industry boundaries. Causal relationships might be unclear, resulting in ´fighting´ against the “unknown unknowns”. There are ever more interconnected parts and variables, leading to higher degrees of complexity. Although a lot of data and knowledge is available, the megatrends create unexpected, unstable and most of all unknown situation, making predictions hard and leaving us with assumptions. Your position within the VUCA world depends on how much you know about the situation and how well you can predict the results of your actions. This explains the flourishing of predictive analytics to try to get a grasp. Next to that, we are in the era of beyond products: service, business model, digital and experience are dominating the business landscape. All this leads to an end for the old, established strategy paradigm.
“ Strategy needs to change because customers and markets are changing faster than ever.”
– Alex Gourlay, Alliance Boots
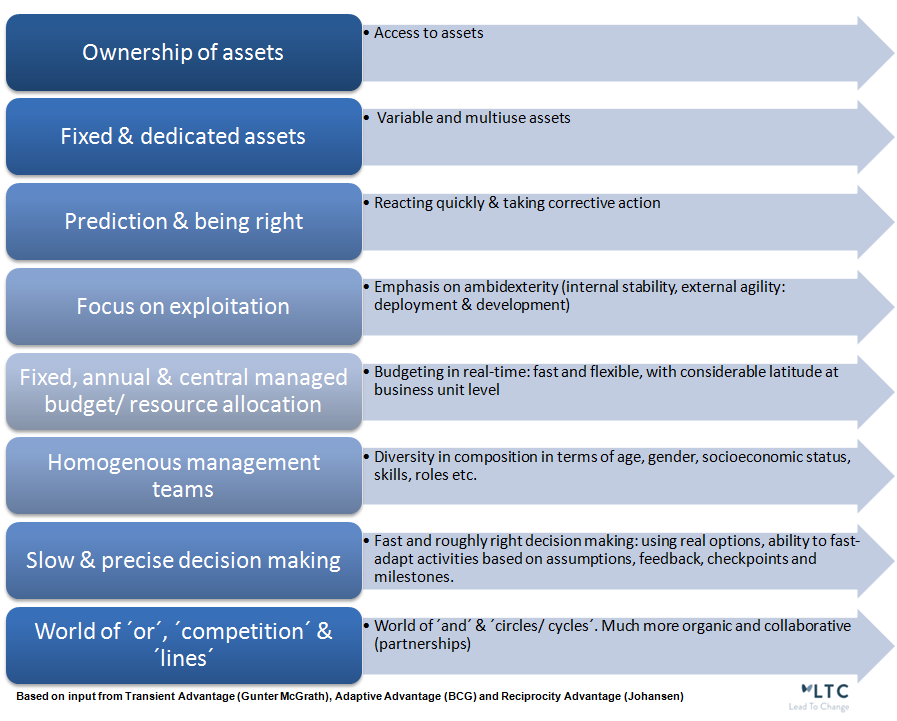
It is time to shift away from Porter´s competitive advantage, based on a differentiation- or cost strategy , and start to open up to concepts as Transient ( temporary) Advantage (Rita Gunther McGrath ), Adaptive Advantage (BCG) and Reciprocity Advantage (Bob Johansen). It is time for a more holistic perspective. Change will boost different temporary waves, to which the strategy should adopt. Only through reconfiguration of assets, people and capabilities one would be able to cope with the transitions. All these concepts are rooted in innovation, leadership skills, strategy and organizational change. They stress the importance of forming partnerships, conducting collaborative experimentation and searching for scalable new business opportunities. In the end, it’s all about creating a systemic, repeatable, and reliable capability that for a while could turn into an advantage.
This asks for a shift of mentality. Below figure provides the main characteristics of the new paradigm. The shift in concept is visualized from left to right, providing a larger degree of freedom and openness to make innovation succeed. How does your company perform on these metrics? To be more adaptive and flexible, decisions on the desired position should be made according to the philosophy in the right box.
Note that the urge to change is nothing new. Attendants showed some nice examples in continuous morphing:
- Nestle transformed from Agro conversion to Nutrition and Health
- Philips, originally known for light bulbs, just announced that they will focus on medical devices.
- DSM from state mines to commodity company to life sciences & materials sciences
Play without any guarantees
It is apparent that innovation and ´conquering the future´ is playing without guarantees and for that accountants hate us. Several theories and strategies where shared to find a ways of governing the process.
The first one was the use of real options. By postponing major commitments, you build in flexibility. Only allocate big resources when the evidence from previous milestones signals that the risk of taking the next step is justified. This is in line with the popular Lean Startup methodology, which has also entered the corporate world. Steve Blank suggests starting with a MVP (minimal valuable product): the minimum elements to make your product/ service deliver value. In this way, failure can be minimized to the front end of innovation; otherwise it will cost you a lot of money.
Budgeting in real time is also closely linked to the transient advantage economy (Gunther McGrath, 2013). It implies that resources should be continually freed up from old advantages and opportunities to fund the developments of new ones. Resources have to be reallocated on an ongoing basis to the process that needs it most at that time, so no yearly fixed budgets. Only then industry change can become an opportunity to exit old businesses and enter new, higher-growth segments. To create transient advantage fluidity in allocation of talent is required, since continuous learning and development is a mechanism to avoid having to fire people when competitive conditions shift. Hence, people should be hired for their learnability: capacity to learn new things.
According to a Chinese proverb ´Sudden danger – hidden opportunity ´, we should keep heads up in that dangerous and changing VUCA world. We just need to conquer it with VUCA answers; Vision, Understanding (qualitative insight and data interpretation) , Clarity and Agility. VUCA answers provide a way to incorporate uncertainty in planning. It is based on reverse engineer the path where to go to: your strategy. The roadmap helps to strengthening foundations for acceleration.
As a counter reaction to the complexity, also the term Frugal Innovation was introduced. A process of reducing the complexity and cost of a good and its production, which is often applied to enter third world countries and offer more social responsible solutions.
To confront the industry wide upheaval and ensure scalability a suggested useful method is ´Seizing the White Space´, focusing on the transformation of existing markets. A four components framework – customer value proposition, profit formula, key resources and key processes- is the basic in which Johson suggests the direction for business model innovations to make the company more agile: achieve transformational growth by fulfilling unmet customer needs in their current markets; serving entirely new customers and creating new markets; and responding to tectonic shifts in market demand, government policy, and technologies that affect entire industries.
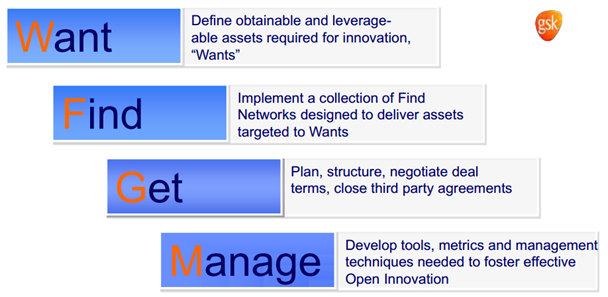
Another seen method is the “Want/ find/ get/ manage process”. Originating from the pharmaceutical sector, the WFGM model starts to be widely adopted in the techscouting landscape.
Important in this cascade is also to get customer insight. What are the felt pains? Which gains can be obtained and what are the encountered inefficiencies? It is recommended to think in functions instead of solutions, because solutions change and the function stays the same. Finding analogies and learning from nature (biomimicry) are good tools for this. Have you ever tried Ask Nature to figure out which functions nature puts in place to solve your customer problems?
Lastly, as in the Next Bank Conference, also the organizational structure was criticized as an inhibiter. The ´wirearchy´ or organic structure was promoted to enhance innovation efforts. As a good source to understand how acceleration is disruption corporations´ basic structures, Kotters new book XLR8 was suggested. Putting the entrepreneurial spirit in the center creates a networked mechanism, which makes the organization more reliable, efficient, fast and agile to maneuver in the faster moving environment.
It is worth to take a minute and figure out: who is the disruptor in your sector? Do you have an overview of the disruptors in your sector and do you follow their developments? Through engineered serendipity you can create partnerships with these disruptors to make sure that you are part of the revolution instead of the dinosaur that is being disrupted.
The CO-Era of Knowledge Sharing Partnerships
Don’t reinvent the wheel! How can you innovate if you don’t know what already exists? What is already evolving in your own industry? Perhaps the solution can already be found. If this is not the case, it is time to start innovating. Usually, the process is from inside to outside, because first the internal knowledge should be leveraged and aligned and from that one could reach out to capture additional insights from own and other sectors.
Especially in larger organizations – whether a multinational, university or research institute – it might be a challenge to find the opportunities and knowledge within. How do you arrange your knowledge management? Some have created monthly Open Innovation meetings to get additional capabilities and insights with partners. Others organize internal conferences, get-togethers, entrepreneurial boothcamps or lunch- and learn sessions. Usually it is a mix of formal and informal touchpoints. However, there is no blueprint.
When a desired function or solution is described, the search starts for experts and scouting the availability and maturity of the envisioned technologies. A lot use a portal/ platform to get in touch; others make use of the WFGM approach to find partners. In general, all speakers agreed that face-to-face contact seems to bring more results. From that emerging business area (EBA) might arise. DSM structured its innovation efforts along 3 EBA lines – biomedical ( bio-interactive applications, therapeutic materials, regenerative medicine, tissue engineering) , biobased products & services, advanced surfaces – which turned out to work quite well resulting in new products and ventures.
Above efforts in knowledge sharing, relationship building and capturing joint value are part of the Open Innovation strategy a company pursues. More and more, it is being referred to as Connected Innovation; putting people, power of the crowd, supplier engagement and trustful partnerships central. Note that the size of network is less important than the activity of the network. Or as Harris & McDonald frame it “It is no longer enough to share information one-to-one with partners. Increasing predictive power rests in positioning yourself at the center of multiple information flows.”
We are heading towards radical collaboration and innovation in the cloud. An nice example is Hue; a personal wireless lightning system from Philips. Hue is completely build on an open strategy, which is based on the community ´Friends of Hue´. Basics were the embracement of the developers community and giving Hue away as a free open source platform. Within weeks developers started to develop many unexpected services and applications . All for free. The big lesson: Hue software is open source, which is great for encouraging third-party app development and stimulate the developer community to create new products with it. It completely embraces the trend of API and found a way to benefit from the IoT. Want to participate? Join the API-application platform; a global infrastructure for collaboration.
In technology scouting, closing the gap between academia and business is the interface of (close to ) ready to use solutions. Science and innovation have to go hand in hand. Companies seek active relationships with universities to tap into their competences and technology platforms. Universities seek for collaboration to shape the valorization flow and impact market solutions. Companies bring external funding and a professional network. Universities offer technical breadth, interdisciplinary research and a long term horizon. At the same time, startups and spin offs also offer interesting features to companies, resulting in larger budgets for corporate venturing. Startups are a source of technical depth, they can fill a competency void, are on top of emerging technologies and often give access to IP.
When entering a collaboration or partnership trust was the most important word. It became apparent that it is key to create the right environment for trust. To really reach out to each other and understand each other an atmosphere should be created in which you are able to agree and disagree, to expose vulnerabilities by sharing what you are not good at. Through exploring those vulnerabilities, you can detect the promising space on which collaboration can be build: you acknowledge that both can´t do it alone – you need each other. When closing innovation partnerships, do it gradually (keep out as long as possible the 50 pages none disclosure agreements). First explore if you really can collaborate. And remember ´the bigger the deal, the smaller the meeting.´
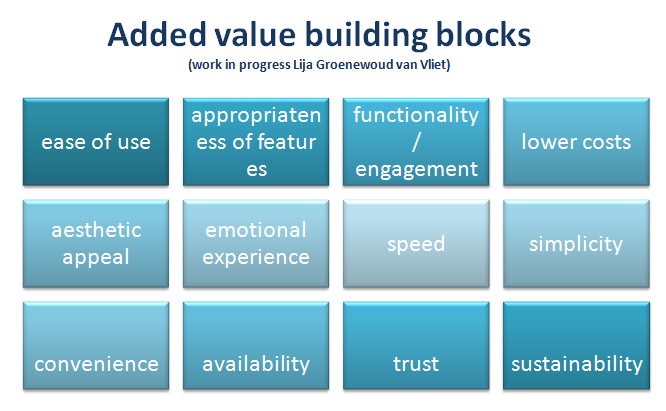
When entering the collaboration, ask yourself: who is going to capture the value of the innovation? Think through the type of value you will generate from the innovation and make sure that your business model is based on that value and not on the byproduct. Currently, I am developing a framework on how to assess the added value one will include in an innovation. It consists of 12 building blocks. Herewith a first outlook, but to be continued.
Connect, dare to share and care!
Having visited several* conferences on the interface of innovation, all come with a BUT why is it such a struggle, a challenge to tap the real potential. And number one is dominantly: culture & attitude. It’s all about encouraging the network of people. Culture defined as intrapreneurship, win-win, “proudly found elsewhere”, dive and take, share and care, Openness, leadership role, risk aversion & reward. Speaker Valerio Nannini introduced a hierarchy of human capabilities at work:
- Level 6: Passion
- Level 5: Creativity
- Level 4: Initiative
- Level 3: Expertise
- Level 2: Diligence
- Level 1: Obedience
For innovation, level 4,5 and 6 count to excel. Furthermore, he described four types of role needed within the innovation process: trendspotter, inventor, mastermind and executive. Especially for the first two, who operate mostly as the intrapreneurs within a company, the passion, creativity and initiative are key to succeed. Rob Kirschbaum added some rules to help them succeed in the corporate jungle:
- Come to work each day willing to be fired
- Forget pride of authorship, spread credit widely
- Honour your sponsors
- Underpromise and overdeliver
- Remember, it is easier to ask for forgiveness than for permission
We haven´t entered innovation maturity. The changing world keeps challenging us and we are still searching for the right way and structures to conquer it. Hence, many more conferences will follow to share experiences. In the future Techscout could benefit from an interactive knowledge sharing tool, where participants directly could upload suggestion and crowdsource ideas. A nice icebreaker in this conference was a gamification to let participants get to know each other better and share experience.
Interested in above topics and activities of the European Networking Group? On April 20th -21st 2015, a follow up event will be organized in Berlin: Innovation Fusion
* some other Heard@ articles covering strategy, innovation and trends:
- Disrupting in the financial sector
- Smart fabrics & wearables
- Six laws of Innovation
- The potential of 3D printing
- Intrapreneurship: ambassadors of change
Image credit: Shutterstock, Lead To Change






Leave a Reply